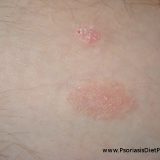
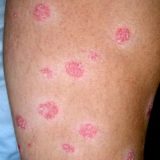
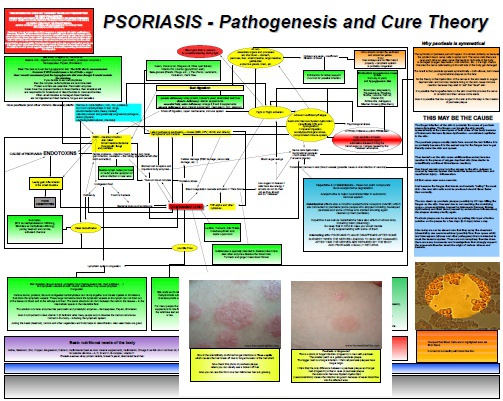
Taurine Decreases Inflammation In Psoriasis
Psoriasis is not the most common term you hear when you read about the effects of taurine on health. You read usually about its positive effects on nervous system, liver (bile production and bile flow), heart but less about anti-inflammatory and possibly anti-psoriatic effects of taurine I am going to present here right now. Psoriasis as you probably know from this blog is caused by Autonomic Nervous System dysfunction which in turn is (usually if not always) caused by systemic…